CSS选择器总结
七、CSS3 属性选择器(上)什么是 CSS3在 CSS2 的基础上拓展、新增的样式CSS3 发展现状移动端支持优于 PC 端CSS3 目前还草案,在不断改进中CSS3 相对 H5,应用非常广泛属性选择器列表属性选择器代码演示button { cursor: pointer; } butt...
2021年3月10日
718字
11 阅读
todo
选择器
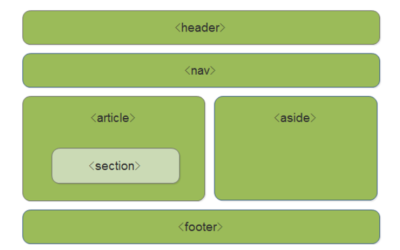
CSS选择器分为基础选择器和复合选择器.
基础选择器
- 标签选择器(元素选择器)
- 类选择器
- id选择器
- 通配符选择器
后代选择器( )
.class h3{
color:red;
font-size:16px;
}子元素选择器(>)
.class>h3{
color:red;
font-size:14px;
}交集选择器(.)
p.one {
/* */
}并集选择器(,)
.one, p , #test {
color: #F00;
} ~ +
- A ~ B表示选择A标签后的所有B标签,但是A和B标签必须有相同的父元素。
- A+B表示选择紧邻在A后面的B元素,且A和B必须拥有相同的父元素,所选到的仅为一个B元素标签
链接伪类选择器
- a:link / 未访问的链接 /
- a:visited / 已访问的链接 /
- a:hover / 鼠标移动到链接上 /
- a:active / 选定的链接 /
- 注意:写的时候,他们的顺序尽量不要颠倒 按照 lvha 的顺序。否则可能引起错误。
/* a是标签选择器 所有的链接 */
a {
font-weight: 700;
font-size: 16px;
color: gray;
}
/* :hover 是链接伪类选择器 鼠标经过 */
a:hover {
color: red;
}CSS3选择器
属性选择器
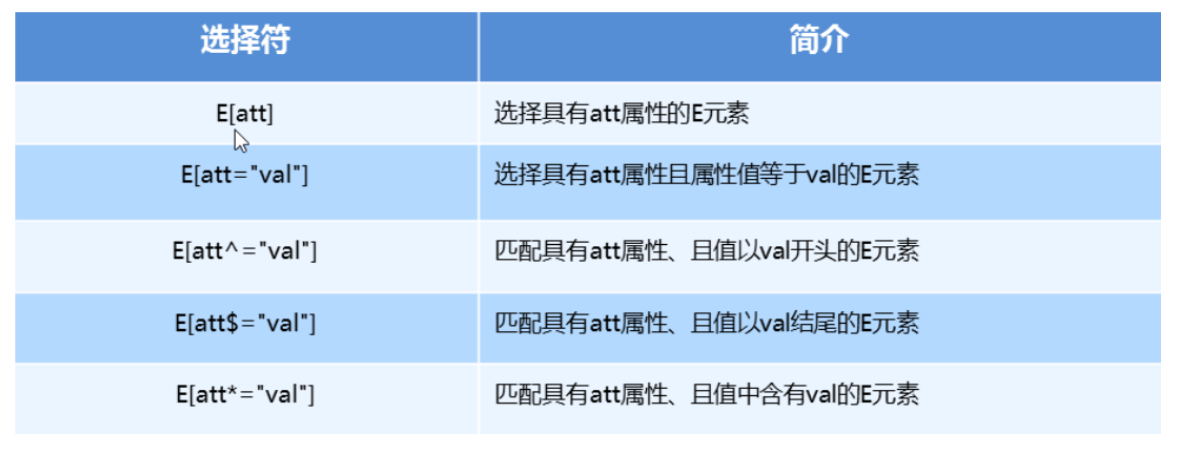
结构伪类选择器
ul li:first-child {
background-color: lightseagreen;
}
ul li:last-child {
background-color: lightcoral;
}
ul li:nth-child(3) {
background-color: aqua;
}nth-child
- 注意:本质上就是选中第几个子元素
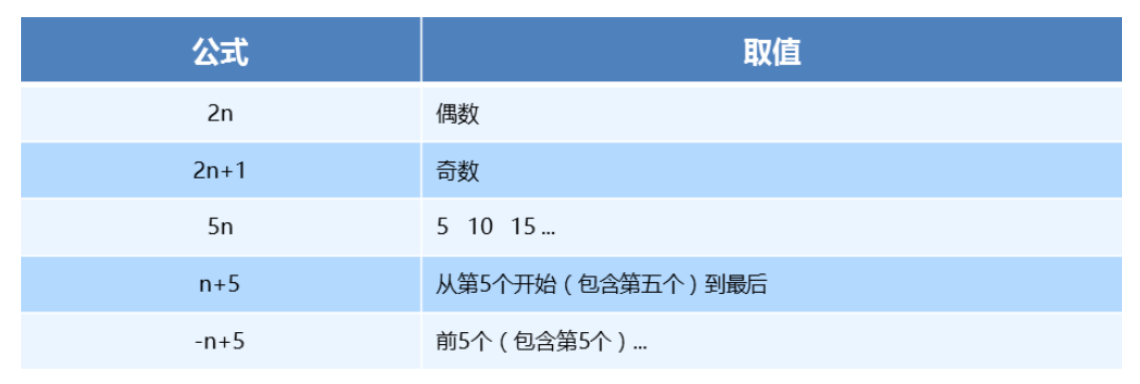
- n 可以是数字、关键字、公式
- n 如果是数字,就是选中第几个
- 常见的关键字有
even偶数、odd奇数 - 常见的公式如下(如果 n 是公式,则从 0 开始计算)
- 但是第 0 个元素或者超出了元素的个数会被忽略
/* 偶数 */
ul li:nth-child(even) {
background-color: aquamarine;
}
/* 奇数 */
ul li:nth-child(odd) {
background-color: blueviolet;
}
/*n 是公式,从 0 开始计算 */
ul li:nth-child(n) {
background-color: lightcoral;
}
/* 偶数 */
ul li:nth-child(2n) {
background-color: lightskyblue;
}
/* 奇数 */
ul li:nth-child(2n + 1) {
background-color: lightsalmon;
}
/* 选择第 0 5 10 15, 应该怎么选 */
ul li:nth-child(5n) {
background-color: orangered;
}
/* n + 5 就是从第5个开始往后选择 */
ul li:nth-child(n + 5) {
background-color: peru;
}
/* -n + 5 前五个 */
ul li:nth-child(-n + 5) {
background-color: tan;
}
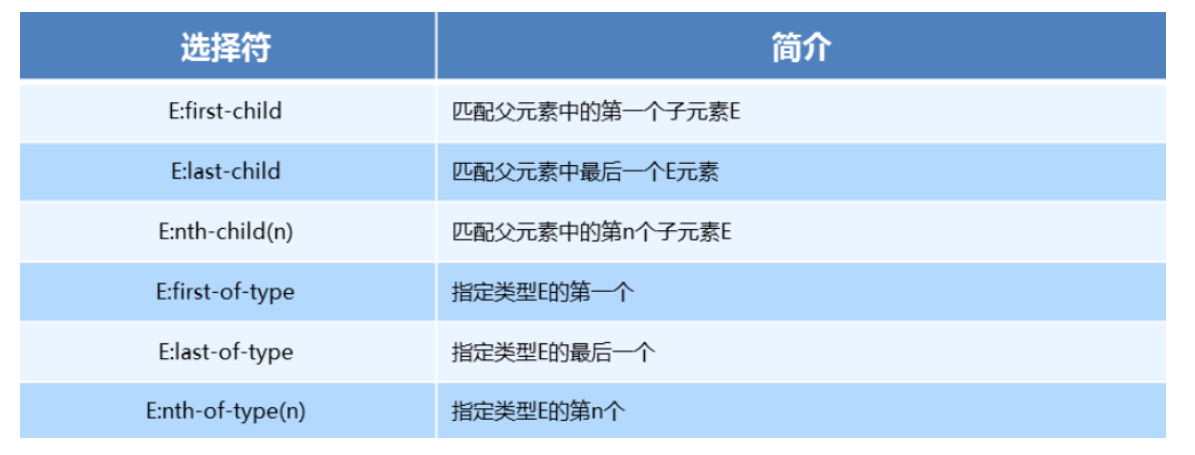
nth-child 和 nt-of-type 的区别
- 代码演示
<style>
div :nth-child(1) {
background-color: lightblue;
}
div :nth-child(2) {
background-color: lightpink;
}
div span:nth-of-type(2) {
background-color: lightseagreen;
}
div span:nth-of-type(3) {
background-color: #fff;
}
</style>- 区别
nth-child选择父元素里面的第几个子元素,不管是第几个类型nt-of-type选择指定类型的元素
伪元素选择器

before和after必须有content属性before在内容前面,after 在内容后面before和after创建的是一个元素,但是属于行内元素- 创建出来的元素在
Dom中查找不到,所以称为伪元素 - 伪元素和标签选择器一样,权重为 1

文章评论区
欢迎留言交流