
莱文斯坦距离(LD)问题
问题描述Levenshtein Distance也称莱文斯坦距离具体形式就是求一个字符串到另一个字符串所需要的最少操作步数,操作形式有:替换字母删除字母插入字母问题分析利用动态规划思想,将其剖析为一个个子问题,用其子问题的解决方式来解决该问题。问题分解出来的子问题存在重叠的情况,这是区分分治算...
2020年10月24日
1.1千字
15 阅读
1 点赞
问题描述
Levenshtein Distance也称莱文斯坦距离
具体形式就是求一个字符串到另一个字符串所需要的最少操作步数,操作形式有:
- 替换字母
- 删除字母
- 插入字母
问题分析
利用动态规划思想,将其剖析为一个个子问题,用其子问题的解决方式来解决该问题。问题分解出来的子问题存在重叠的情况,这是区分分治算法的不同。

莱文斯坦的公式化表述为:
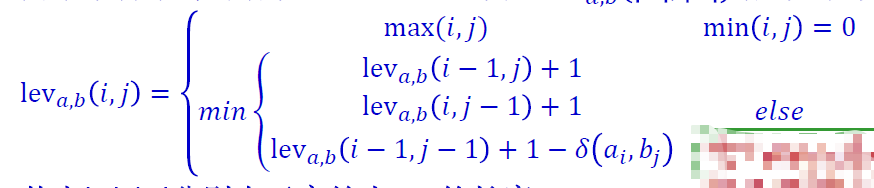
下面利用表格的形式来步步推出该字母所需要达到相应的目标字母序列的步数。
s | o | n | ||
0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | |
s | 1 | 0 | 1 | 2 |
u | 2 | 1 | 1 | 2 |
n | 3 | 2 | 2 | 1 |
记横(son)为i字符串序列,纵(sun)为j字符串序列。需要完成的字符串变换为i->j。现举例格子数值该怎么填:
当到了第三行第三列的那一格,需要完成s->s,有三种情况可以选择
- 左操作(i-1,j):删除s字符然后插入s字符===操作步数两步
- 上操作(i,j-1):插入s字符然后删除s字符===操作步数两步
- 左上操作(i-1,j-1):替换步骤,因为这个元素相同,故===操作步数零部
然后选取上述三种情况最短步数的数值0
然后再看第三行第四列,需要完成so->s,
- 左操作:删除o===一步
- 上操作:插入s删除so===三步
- 做上操作:替换s删除o===两步
综上应该填1
其他格子也一样以上述方法填写。
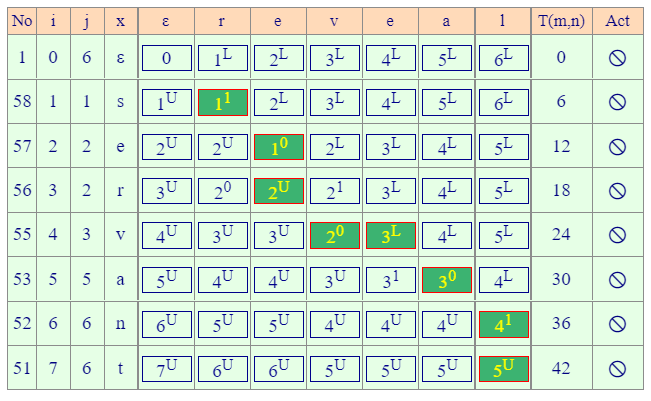
有个作业遗留问题,在CAAIS里面每个得出的值右上标的 U L 0 1 这些的依次顺序是怎么个顺序?
代码实现
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
#include<iostream>
#include<ctime>
const int LEN_NAME=100;
namespace NS_LSEditDist {
using namespace std;
void Initialization(const string &x, const string &y);
int GetLSEditDist(const string &x, const string &y);
void GetLSEdits(const string &x, const string &y);
void Output(const string &x, const string &y, int OptD);
void OutputE(const string &x, const string &y);
void OutputP(const string &x, const string &y);
static int m, n;
static vector<vector<int>> E;
static vector<vector<char>> P;
static string xe, ye;
void LSEditDistCaller(const string &x, const string &y)
{
Initialization(x, y);
int OptD = GetLSEditDist(x, y);
GetLSEdits(x, y);
Output(x, y, OptD);
}
int GetLSEditDist(const string &x, const string &y)
{
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++)
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++)
{
E[i][j] = min(E[i - 1][j] + 1,
min(E[i][j - 1] + 1,
E[i - 1][j - 1] + (x[i - 1] != y[j - 1])));
if (E[i][j] == E[i - 1][j] + 1)
P[i][j] = 'U';
else if (E[i][j] == E[i][j - 1] + 1)
P[i][j] = 'L';
else if (x[i - 1] != y[j - 1])
P[i][j] = '1';
}
return E[m][n];
}
void GetLSEdits(const string &x, const string &y)
{
int i = m, j = n;
while (i > 0 || j > 0)
{
if (P[i][j] == '0' || P[i][j] == '1')
{
xe.insert(0, 1, x[i - 1]);
ye.insert(0, 1, y[j - 1]);
i--; j--;
}
else if (P[i][j] == 'U')
{
xe.insert(xe.begin(), x[i - 1]);
ye.insert(ye.begin(), '-');
i--;
}
else
{
xe.insert(xe.begin(), '-');
ye.insert(ye.begin(), y[j - 1]);
j--;
}
}
}
void Initialization(const string &x, const string &y)
{
m = x.length();
n = y.length();
E.clear();
E.resize(m + 1, vector<int>(n + 1, 0));
P.clear();
P.resize(m + 1, vector<char>(n + 1, '0'));
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++)
{
E[0][j] = j;
P[0][j] = 'L';
}
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++)
{
E[i][0] = i;
P[i][0] = 'U';
}
xe.clear();
ye.clear();
}
void Output(const string &x, const string &y, int OptD)
{
printf("Levenshtein distance: \n");
printf("Strings: %s, %s\n\n", x.c_str(), y.c_str());
OutputE(x, y);
OutputP(x, y);
printf("Distance: %d\n", OptD);
printf("Edited strings:\n");
for (auto c : xe)
printf("%2c", c);
printf("\n");
for (auto c : ye)
printf("%2c", c);
printf("\n\n");
}
void OutputE(const string &x, const string &y)
{
printf(" E ");
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++)
printf("%2c", y[j]);
printf("\n");
for (int i = 0; i <= m; i++)
{
if (i == 0)
printf(" ");
else
printf("%2c", x[i - 1]);
for (int j = 0; j <= n; j++)
{
printf("%2d", E[i][j]);
}
printf("\n");
}
printf("\n");
}
void OutputP(const string &x, const string &y)
{
printf(" P ");
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++)
printf("%2c", y[j]);
printf("\n");
for (int i = 0; i <= m; i++)
{
if (i == 0)
printf(" ");
else
printf("%2c", x[i - 1]);
for (int j = 0; j <= n; j++)
{
printf("%2c", P[i][j]);
}
printf("\n");
}
printf("\n");
}
} //namespace NS_LSEditDist
char *rand_str(char *str,const int len)
{
int i;
for(i=0;i<len;++i)
str[i]='a'+rand()%26;
str[++i]='\0';
return str;
}
using namespace NS_LSEditDist;
int main()
{
vector<vector<string>> abs = {
{ "water", "wheat" },
{ "servant", "reveal" }
};
for (auto ab : abs)
{
string a = ab[0];
string b = ab[1];
LSEditDistCaller(a, b);
}
cout<<"两个100位字符串的LevenShtein距离:"<<endl;
srand(time(NULL));
int i;
char name[LEN_NAME+1];
string x = rand_str(name,LEN_NAME);
string y = rand_str(name,LEN_NAME);
cout<<"字符串1:"<<x<<endl;
cout<<"字符串2:"<<y<<endl;
LSEditDistCaller(x, y);
}
文章评论区
欢迎留言交流