
图的遍历——DFS(深度优先)、BFS(广度优先)
前言:用邻接矩阵和邻接表两种图的存储形式实现DFS、BFS算法,并附例子实现。总的来说,邻接矩阵比较好处理,没有邻接表处理那么复杂,但是数组永远不能规避的一个缺点就是内存的占用较邻接表高。一、深度优先搜索算法(Depth-First-Search)算法说明访问步骤:访问顶点v;依次从v的未被访...
前言:用邻接矩阵和邻接表两种图的存储形式实现DFS、BFS算法,并附例子实现。
总的来说,邻接矩阵比较好处理,没有邻接表处理那么复杂,但是数组永远不能规避的一个缺点就是内存的占用较邻接表高。
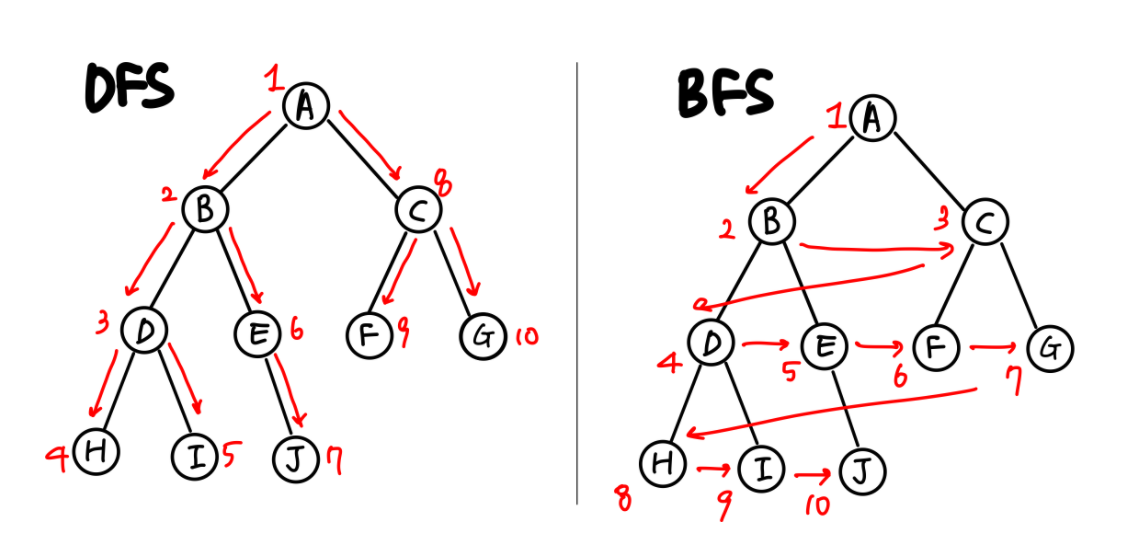
一、深度优先搜索算法(Depth-First-Search)
算法说明
访问步骤:
- 访问顶点v;
- 依次从v的未被访问的邻接点出发,对图进行深度优先遍历;直至图中和v有路径相通的顶点都被访问;
- 若此时图中尚有顶点未被访问,则从一个未被访问的顶点出发,重新进行深度优先遍历,直到图中所有顶点均被访问过为止。
核心代码就是利用递归,以及标志数组的设定,每次访问数组元素的那一行,对那行链表进行遍历,每遍历一个链表结点,就将“其”所在的那个数组元素“点亮”。如果标志数组里面的所有元素都被访问了,说明遍历完了
深度优先搜索类似于树里面遍历算法当中的先序遍历。
邻接矩阵的DFS代码
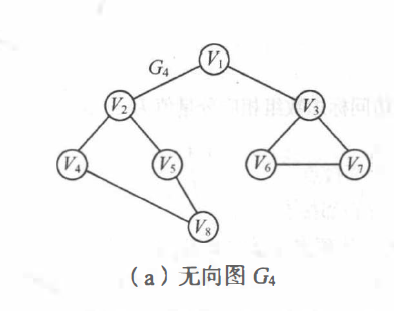
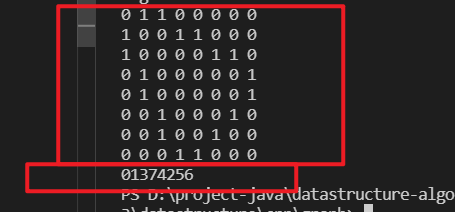
以这个无向图为例
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define MVNum 100
#define MaxInt 32767
typedef char VerTexType;
typedef int ArcType;
/**
* 邻接矩阵存储形式
*/
typedef struct {
/* data */
VerTexType vexs[MVNum]; //顶点表
ArcType arcs[MVNum][MVNum]; //邻接矩阵
int vexnum, arcnum; //图的当前顶点和边数
}AMGraph;
/**
* 确定v在G中的位置,即顶点数组的下标
*/
int LocateVex(AMGraph &G, char v) {
for (int i = 0; i < G.vexnum;i++) {
if (v == G.vexs[i]){
return i;
}
}
}
/**
* 如果创建无向图
*/
void CreateUDN(AMGraph &G) {
// 采用邻接矩阵表示法,创建无向图G
cout << "请输入顶点数和边数:" << endl;
cin >> G.vexnum >> G.arcnum; //输入顶点数和边数
// 初始化顶点
for (int i = 0; i < G.vexnum;i++){
cout << "请输入第" << i << "个顶点值" << endl;
cin >> G.vexs[i];
}
// 初始化邻接矩阵的边的权值为最大值
for (int i = 0; i < G.vexnum;i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < G.vexnum;j++) {
G.arcs[i][j] = 0;
}
}
// 构造邻接矩阵
for (int k = 0; k < G.arcnum;k++) {
cout << "请输入每条边所依附的顶点:" << endl;
char v1, v2;
int w = 1; //一条边所依附的顶点和权值
cin >> v1 >> v2;
int i = LocateVex(G, v1);
int j = LocateVex(G, v2);
G.arcs[i][j] = w;
G.arcs[j][i] = w;
}
}
/**
* 打印输出图
*/
void Display(AMGraph &G) {
for (int i = 0; i < G.vexnum;i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < G.vexnum;j++) {
cout << G.arcs[i][j] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
}
//----邻接矩阵的DFS遍历----
//访问标志数组,其初值为false
bool visited[MVNum];
/**
* 图G为邻接矩阵类型,从第v个顶点出发深度优先搜索遍历图G
*/
void DFS_AM(AMGraph &G, int v) {
//访问第v个顶点,并置访问标志数组相应分量值为true
cout<<v;
visited[v] = true;
//依次检查邻接矩阵v所在的行
for(int w = 0; w < G.vexnum; w++)
//G.arcs[v][w] != 0表示w是v的邻接点,!visited[w]表示未访问到
if((G.arcs[v][w] != 0) && (!visited[w]))
DFS_AM(G, w); //递归调用DFS_AM
}
/**
* 图G的储存类型任意,对非连通图G做深度优先遍历
*/
void DFSTraverse(AMGraph &G) {
//访问标志数组初始化
for(int v = 0; v < G.vexnum; v++)
visited[v] = false;
//循环调用DFS
for(int v = 0; v < G.vexnum; v++)
if(!visited[v])
DFS_AM(G, v); //对尚未访问的顶点调用DFS
}
int main() {
AMGraph test;
CreateUDN(test);
Display(test);
DFSTraverse(test);
return 0;
}
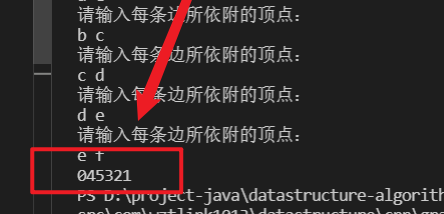
邻接表的DFS代码
举之前上课的一张PPT例子(元素插入为后插法)
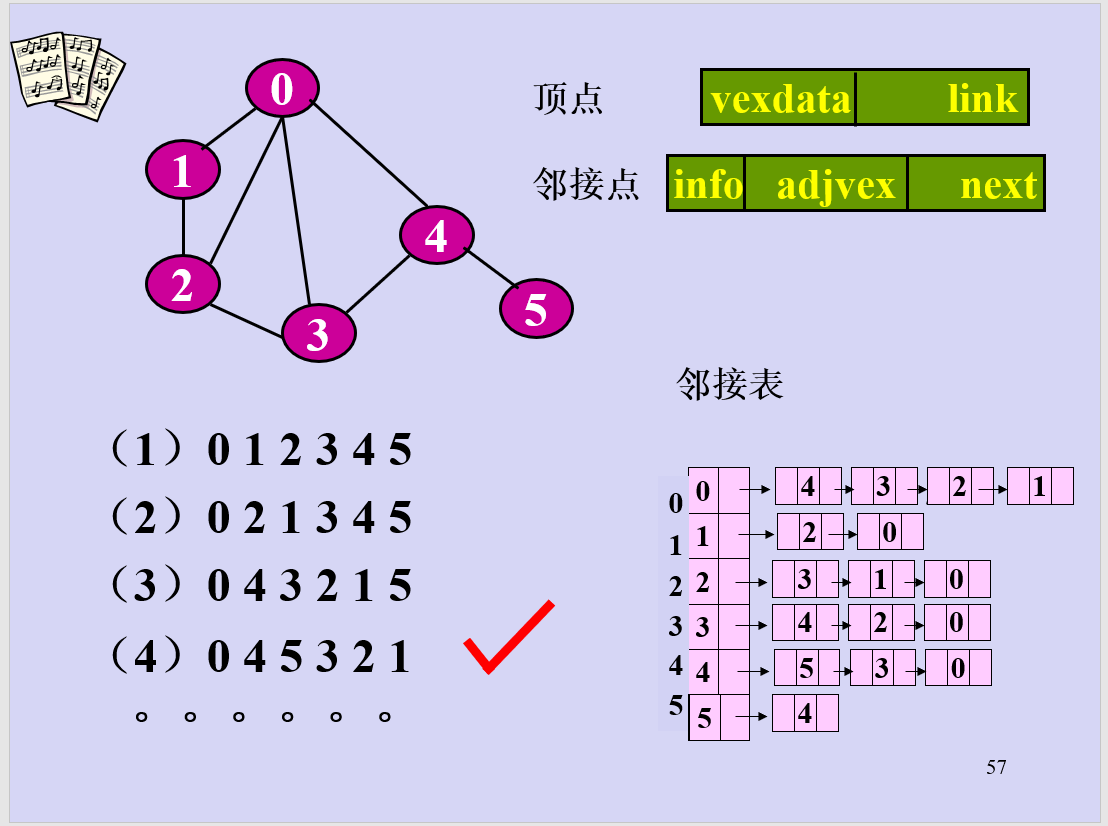
结果
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define MVNum 100
#define MaxInt 32767
typedef char VerTexType;
typedef int OtherInfo;
/**
* 邻接表存储
*/
/**
* 存储结构
*/
typedef struct ArcNode { //边结点
int adjvex; //该边所指向的结点的位置
struct ArcNode *nextarc; //指向下一条边的指针
OtherInfo info; //和边相关的其他信息
}ArcNode;
typedef struct VNode { //顶点信息
VerTexType data; //数据域,存放顶点vi的名称或其他有关信息
ArcNode *firstarc; //指向第一条依附该顶点的边的指针
}VNode, AdjList[MVNum]; //AdjList表示邻接表的类型
typedef struct {
AdjList vertices;
int vexnum, arcnum; //图当前的顶点数和边数
}ALGragh; //邻接表(Adjacency List)
/**
* 找到v顶点在图的顶点数组中的位置
*/
int LocateVex(ALGragh &G, char v) {
for (int i = 0; i < G.vexnum;i++) {
if (v == G.vertices[i].data) {
return i;
}
}
}
/**
* 邻接表创建无向图
*/
void CreateUDG(ALGragh &G) {
cout << "请输入顶点数和边数:" << endl;
cin >> G.vexnum >> G.arcnum; // 邻接表的顶点数和边数
// 初始化顶点数组
for (int i = 0; i < G.vexnum;i++) {
cin >> G.vertices[i].data; // 初始化顶点数组里面的结点data
G.vertices[i].firstarc = NULL; // 初始化顶点数组里面的结点next域
}
// 初始化所有的边
for (int k = 0; k < G.arcnum;k++) {
char v1, v2;
cout << "请输入每条边所依附的顶点:" << endl;
cin >> v1 >> v2;
int i = LocateVex(G, v1); // 找到v1在顶点数组的下标
int j = LocateVex(G, v2); // 找到v2在顶点数组的下标
// 下面建立p1和p2是因为无向图,如果是有向图就没必要了只需要p1
// 前插
ArcNode *p1 = new ArcNode;
p1->adjvex = j;
p1->nextarc = G.vertices[i].firstarc;
G.vertices[i].firstarc = p1;
ArcNode *p2 = new ArcNode;
p2->adjvex = i;
p2->nextarc = G.vertices[j].firstarc;
G.vertices[j].firstarc = p2;
}
}
/**
* 打印输出图
*/
void Display(ALGragh &G) {
for (int i = 0; i < G.vexnum;i++) {
cout << "结点" << i << ":";
// 复制选中的节点数组中的结点
VNode p;
p = G.vertices[i];
if (p.firstarc != NULL){
ArcNode *temp;
temp = G.vertices[i].firstarc;
while (temp != NULL) {
cout << temp->adjvex<<" ";
temp = temp->nextarc;
}
cout << "\n";
}
}
}
//----邻接表的DFS遍历----
bool visited[MVNum]; //访问标志数组,其初值为false
void DFS_AL(ALGragh G, int v)
{//图G为邻接表类型,从从第v个顶点出发深度优先搜索遍历图G
cout<<v; //访问第v个顶点,并置访问标志数组相应分量值为true
visited[v] = true;
ArcNode *p;
p = G.vertices[v].firstarc; //p指向v的边链表的第一个边结点
while(p != NULL)
{
int w = p->adjvex; //w是v的邻接点
if(!visited[w]) //如果w未访问
DFS_AL(G, w); //递归调用DFS_AL
p = p->nextarc; //p指向下一个结点
}
}
void DFSTraverse(ALGragh G)
{//图G的储存类型任意,对非连通图G做深度优先遍历
for(int v = 0; v < G.vexnum; v++) //访问标志数组初始化
visited[v] = false;
for(int v = 0; v < G.vexnum; v++) //循环调用DFS
if(!visited[v])
DFS_AL(G, v); //对尚未访问的顶点调用DFS
}
int main() {
ALGragh test;
CreateUDG(test);
// Display(test);
DFSTraverse(test);
}二、广度优先搜索算法(Breadth-First-Search)
算法说明
从某个顶点V0出发,并在访问此顶点之后依次访问V0的所有未被访问过的邻接点,之后按这些顶点被访问的先后次序依次访问它们的邻接点,直至图中所有和V0有路径相通的顶点都被访问到。
若此时图中尚有顶点未被访问,则另选图中一个未曾被访问的顶点作起始点,重复上述过程,直至图中所有顶点都被访问到为止。
在树遍历中类似层次遍历。
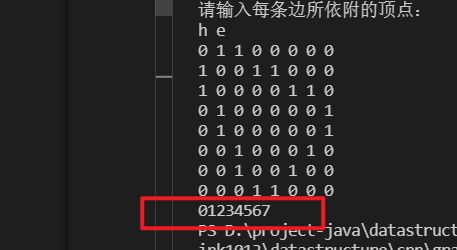
邻接矩阵的BFS代码
还是这个例子

#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define MVNum 100
#define MaxInt 32767
typedef char VerTexType;
typedef int ArcType;
/**
* 邻接矩阵的bfs代码
*/
typedef struct {
/* data */
VerTexType vexs[MVNum]; //顶点表
ArcType arcs[MVNum][MVNum]; //邻接矩阵
int vexnum, arcnum; //图的当前顶点和边数
}AMGraph;
/**
* 确定v在G中的位置,即顶点数组的下标
*/
int LocateVex(AMGraph &G, char v) {
for (int i = 0; i < G.vexnum;i++) {
if (v == G.vexs[i]){
return i;
}
}
}
/**
* 创建无向网
* 如果创建无向图
*/
void CreateUDN(AMGraph &G) {
// 采用邻接矩阵表示法,创建无向图G
cout << "请输入顶点数和边数:" << endl;
cin >> G.vexnum >> G.arcnum; //输入顶点数和边数
// 初始化顶点
for (int i = 0; i < G.vexnum;i++){
cout << "请输入第" << i << "个顶点值" << endl;
cin >> G.vexs[i];
}
// 初始化邻接矩阵的边的权值为最大值
for (int i = 0; i < G.vexnum;i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < G.vexnum;j++) {
G.arcs[i][j] = 0;
}
}
// 构造邻接矩阵
for (int k = 0; k < G.arcnum;k++) {
cout << "请输入每条边所依附的顶点:" << endl;
char v1, v2;
int w = 1; //一条边所依附的顶点和权值
cin >> v1 >> v2;
int i = LocateVex(G, v1);
int j = LocateVex(G, v2);
G.arcs[i][j] = w;
G.arcs[j][i] = w;
}
}
/**
* 打印输出图
*/
void Display(AMGraph &G) {
for (int i = 0; i < G.vexnum;i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < G.vexnum;j++) {
cout << G.arcs[i][j] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
}
//----邻接矩阵的BFS遍历----
bool visited[MVNum];
void BFS_AM(AMGraph G, int v)
{//按广度优先非递归遍历连通图G
cout<<v;
visited[v] = true; //访问第v个顶点,并置访问标志数组相应分量值为true
queue<int> Q;
Q.push(v);
while(!Q.empty())
{
int u = Q.front(); //队头元素出队并置为u
Q.pop();
for(int w = 0; w < G.vexnum; w++)
if((G.arcs[u][w] != 0) && (!visited[w])) //G.arcs[v][w] != 0表示w是v的邻接点,!visited[w]表示未访问到 //w为u的尚未访问的邻接顶点
{
cout<<w;
visited[w] = true; //访问w,并置访问标志数组相应分量值为true
Q.push(w); //w进队
}
}
}
void BFSTraverse(AMGraph &G) {
//访问标志数组初始化
for(int v = 0; v < G.vexnum; v++)
visited[v] = false;
//循环调用BFS
for(int v = 0; v < G.vexnum; v++)
if(!visited[v])
BFS_AM(G, v); //对尚未访问的顶点调用BFS
}
int main() {
AMGraph test;
CreateUDN(test);
Display(test);
// DFSTraverse(test);
BFSTraverse(test);
return 0;
}
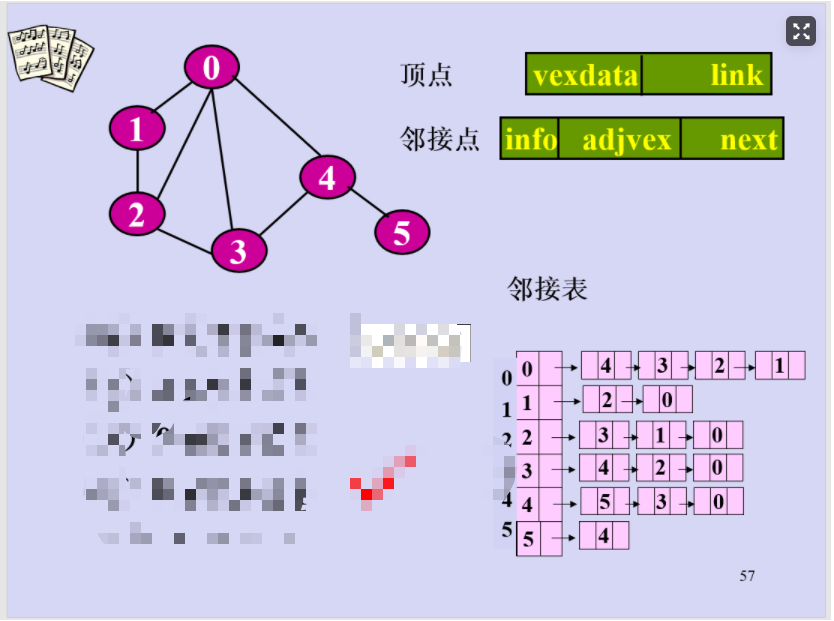
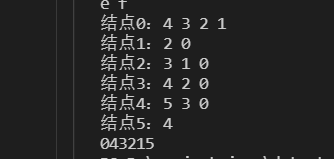
邻接表的BFS代码
还用和DFS一样的例子
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define MVNum 100
#define MaxInt 32767
typedef char VerTexType;
typedef int OtherInfo;
/**
* 邻接表的bfs代码
*/
/**
* 存储结构
*/
typedef struct ArcNode { //边结点
int adjvex; //该边所指向的结点的位置
struct ArcNode *nextarc; //指向下一条边的指针
OtherInfo info; //和边相关的其他信息
}ArcNode;
typedef struct VNode { //顶点信息
VerTexType data; //数据域,存放顶点vi的名称或其他有关信息
ArcNode *firstarc; //指向第一条依附该顶点的边的指针
}VNode, AdjList[MVNum]; //AdjList表示邻接表的类型
typedef struct {
AdjList vertices;
int vexnum, arcnum; //图当前的顶点数和边数
}ALGraph; //邻接表(Adjacency List)
/**
* 找到v顶点在图的顶点数组中的位置
*/
int LocateVex(ALGraph &G, char v) {
for (int i = 0; i < G.vexnum;i++) {
if (v == G.vertices[i].data) {
return i;
}
}
}
/**
* 邻接表创建无向图
*/
void CreateUDG(ALGraph &G) {
cout << "请输入顶点数和边数:" << endl;
cin >> G.vexnum >> G.arcnum; // 邻接表的顶点数和边数
// 初始化顶点数组
for (int i = 0; i < G.vexnum;i++) {
cin >> G.vertices[i].data; // 初始化顶点数组里面的结点data
G.vertices[i].firstarc = NULL; // 初始化顶点数组里面的结点next域
}
// 初始化所有的边
for (int k = 0; k < G.arcnum;k++) {
char v1, v2;
cout << "请输入每条边所依附的顶点:" << endl;
cin >> v1 >> v2;
int i = LocateVex(G, v1); // 找到v1在顶点数组的下标
int j = LocateVex(G, v2); // 找到v2在顶点数组的下标
// 下面建立p1和p2是因为无向图,如果是有向图就没必要了只需要p1
// 前插
ArcNode *p1 = new ArcNode;
p1->adjvex = j;
p1->nextarc = G.vertices[i].firstarc;
G.vertices[i].firstarc = p1;
ArcNode *p2 = new ArcNode;
p2->adjvex = i;
p2->nextarc = G.vertices[j].firstarc;
G.vertices[j].firstarc = p2;
}
}
/**
* 打印输出图
*/
void Display(ALGraph &G) {
for (int i = 0; i < G.vexnum;i++) {
cout << "结点" << i << ":";
// 复制选中的节点数组中的结点
VNode p;
p = G.vertices[i];
if (p.firstarc != NULL){
ArcNode *temp;
temp = G.vertices[i].firstarc;
while (temp != NULL) {
cout << temp->adjvex<<" ";
temp = temp->nextarc;
}
cout << "\n";
}
}
}
//----邻接表的BFS遍历----
bool visited[MVNum];
int FirstAdjvex(ALGraph& G, int u)
{
int w = G.vertices[u].firstarc->adjvex;
return w;
}
int NextAdjVex(ALGraph& G, int u, int w)
{
ArcNode *temp = G.vertices[u].firstarc;
while (temp->adjvex != w)
{
temp = temp->nextarc;
}
if (temp->nextarc)
return temp->nextarc->adjvex;
else
return -1;
delete temp;
}
void BFS_AL(ALGraph& G, int v){
cout << v;
visited[v] = true;
queue<int> Q;
Q.push(v);
int u = v;
while (!Q.empty()){
u = Q.front();
Q.pop();
for (int w = FirstAdjvex(G, u); w >= 0; w = NextAdjVex(G, u, w)){
if (!visited[w]){
cout <<w;
visited[w] = true;
Q.push(w);
}
}
}
}
void BFSTraverse(ALGraph &G) {
//访问标志数组初始化
for(int v = 0; v < G.vexnum; v++)
visited[v] = false;
//循环调用BFS
for(int v = 0; v < G.vexnum; v++)
if(!visited[v])
BFS_AL(G, v); //对尚未访问的顶点调用BFS
}
int main() {
ALGraph test;
CreateUDG(test);
Display(test);
BFSTraverse(test);
}【插眼】为啥我写的一个函数不需要队列也可以???直接将顶点数组的一个元素后面接的链表遍历不就好了,然后再遍历标志数组元素值部位true的不就好了。。。为啥要压队列呀?
莫不是哪里有隐藏的bug,插个眼!!!

【拔眼】这样是一种特殊情况,只适合图的各个结点是按照层次标号的,并且放入标志数组也是按照顺序放入的……
插眼代码如下:
void BFS_AL(ALGraph &G, int v)
{//按广度优先非递归遍历连通图G
cout<<v;
visited[v] = true; //访问第v个顶点,并置访问标志数组相应分量值为true
ArcNode *p;
p = G.vertices[v].firstarc;
if (p != NULL) {
while(p != NULL) {
if (!visited[p->adjvex]){
cout << p->adjvex;
}
visited[p->adjvex] = true;
p = p->nextarc;
}
}
}
文章评论区
欢迎留言交流